How Many Tcp Connections Can A Windows Service Handle Windows Server 2012
TCP/IP is the backbone for Microsoft Windows networks. It is required for internetwork communications and for accessing the Net. Earlier y'all tin implement TCP/IP networking, you should understand IP addressing conventions, subnetting options, and proper noun-resolution techniques—all of which are covered in this chapter from Windows Server 2012 R2 Within Out: Services, Security, & Infrastructure.
- Navigating networking in Windows Server 2012 R2
- Using TCP/IP
- Understanding IPv4 addressing
- Special IPv4 addressing rules
- Using subnets and subnet masks
- Getting and using IPv4 addresses
- Understanding IPv6
- Agreement name resolution
TCP/IP is a protocol suite consisting of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP). TCP is a connection-oriented protocol designed for reliable end-to-end communications. IP is an internetworking protocol that is used to route packets of data called datagrams over a network. An IP datagram consists of an IP header and an IP payload. The IP header contains data virtually routing the datagram, including source and destination IP addresses. The IP payload contains the actual data being sent over the network.
TCP/IP is the backbone for Microsoft Windows networks. It is required for internetwork communications and for accessing the Cyberspace. Before you can implement TCP/IP networking, you lot should empathise IP addressing conventions, subnetting options, and name-resolution techniques—all of which are covered in this affiliate.
Navigating networking in Windows Server 2012 R2
The networking features in Windows Server 2012 R2 are dissimilar from those in early releases of Windows. Windows Server 2012 R2 has a suite of networking tools, including the following:
- Network Explorer. Provides a fundamental console for browsing computers and devices on the network
- Network And Sharing Eye. Provides a key console for viewing and managing a calculator'southward networking and sharing configuration
- Windows Network Diagnostics. Provides automated diagnostics to help diagnose and resolve networking issues
Before discussing how these networking tools are used, we must outset look at the features on which these tools rely:
- Network Discovery. Controls the ability to see other computers and devices
- Network Location Awareness. Reports changes in network connectivity and configuration
The network discovery settings of the figurer you are working with decide the computers and devices you can browse or view in networking tools. Discovery settings piece of work in conjunction with a figurer'due south Windows Firewall to either block or allow the post-obit:
- Discovery of network computers and devices
- Discovery of your computer past others
Network discovery settings are meant to provide the appropriate level of security for each of the diverse categories of networks to which a reckoner tin connect. Three categories of networks are defined for servers:
- Domain Network. Intended as a designation for a network in which computers are connected to the corporate domain to which they are joined
- Individual Network. Intended every bit a designation for a network in which computers are configured as members of a homegroup or workgroup and are non connected direct to the public Internet
- Public Network. Intended as a designation for a guest network in a public place, such as a coffee shop or drome, rather than for an internal network
In domains, y'all tin enable discovery on domain controllers to view fellow member computers. On member computers, you can enable discovery to see other member computers. With computers running nonserver versions of Windows, both homegroups and workgroups are available on individual networks. Homegroups have special sharing settings that are not available in workgroups.
Because a computer saves settings separately for each category of network, you lot can use unlike cake and permit settings for each network category. When you connect to a network for the first fourth dimension, Windows automatically sets the network category based on the computer's network settings. If the computer has multiple network adapters, the adapters tin be connected to different networks and, therefore, can exist assigned different network categories.
Based on the network category, Windows Server 2012 R2 automatically configures settings that turn discovery either on or off. You can manage these settings also. Regardless of whether network discovery was managed automatically and configured manually, the On (Enabled) state means the following:
- The computer can discover other computers and devices on the network.
- Other computers on the network tin can discover the computer.
The Off (Disabled) country means the following:
- The computer tin can't find other computers and devices on the network.
- Other computers on the network can't discover the computer.
Network Explorer, shown in Figure 2-ane, displays a list of discovered computers and devices on the network. In any File Explorer view, yous can access Network Explorer by tapping or clicking the leftmost choice button in the address list and then borer or clicking Network. The computers and devices listed in Network Explorer depend on the network discovery settings of the computer.
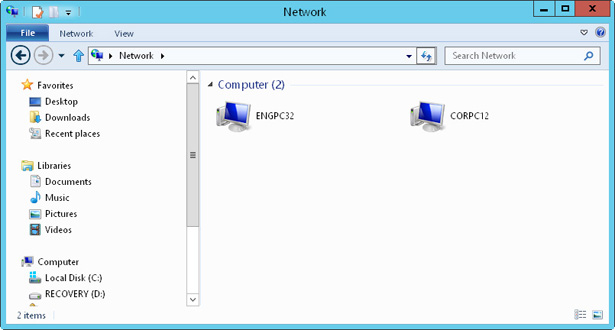
Figure 2-1 Use Network Explorer to browse network resources.
If discovery is blocked, you'll see a note almost this. When you tap or click the alert message, you can enable network discovery by selecting Plow On Network Discovery And File Sharing. This opens the appropriate Windows Firewall ports so that network discovery is immune. If no other changes take been fabricated with regard to network discovery, the computer will exist in the discovery-just state. You need to manually configure the sharing of printers, files, and media, as discussed in Chapter 18, "Managing file sharing," in Windows Server 2012 R2 Inside Out: Configuration, Storage, & Essentials (Microsoft Press, 2014).
When you endeavour to enable network discovery for a network identified every bit public, yous'll encounter an boosted prompt with options for making the network a private network or turning on network discovery and file sharing for all public networks. Generally, you don't want to turn on network discovery and file sharing on public networks because this can open the computer to attack. Therefore, if the computer is actually connected to a public (open) network, click Cancel and do not plough on network discovery. Otherwise, if the figurer is continued to an unidentified individual network, select the option for making the network a private network.
Network And Sharing Centre, shown in Figure 2-2, provides the current network status and an overview of the electric current network configuration. In Control Panel yous tin admission Network And Sharing Center by tapping or clicking View Network Status And Tasks nether the Network And Net heading. In Network Explorer, tap or click Network on the toolbar and so tap or click Network And Sharing Eye.
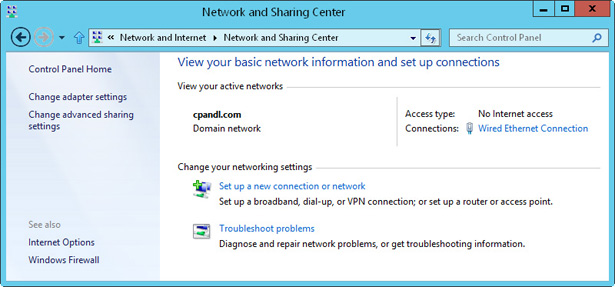
Figure two-2 View and manage network settings with Network And Sharing Centre.
Network And Sharing Center lists the electric current network by name and provides an overview of the network, including the category of the current network as Domain Network, Individual Network, or Public Network. The Admission Blazon field specifies whether and how the computer is continued to its electric current network as No Internet Access or Net Admission. The Connections field shows the proper name of the Local Area Connection being used to connect to the current network. If you tap or click the connection, yous can view the connexion condition in the related Status dialog box.
Windows assigns the public category to any unidentified network, even on domain-joined computers. In Network And Sharing Centre, the network adapter used to connect to the domain should identify the domain and show the network category as Domain Network. However, if a computer'south TCP/IP settings aren't set correctly, Windows might misidentify a network every bit public or individual rather than as a domain network. To resolve this, modify the network adapter's TCP/IP settings. When y'all enter the correct TCP/IP settings, Windows attempts to identify the network again and should set the network category correctly.
Windows might occasionally identify multiple networks on a computer with only one network adapter. Oft the quickest solution for this mixed-state problem is to disable and then enable the network adapter. In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Modify Adapter Settings. Side by side, tap or click the network adapter and then tap or click Disable This Network Device. Finally, tap or click Enable This Network Device.
If a computer has multiple network adapters connected to dissimilar networks, Windows Server might incorrectly identify the connected networks as either public or private instead of domain every bit well. Often the quickest solution for this mixed-country problem is to disable the network adapter that isn't connected to the corporate network. For example, during development testing, I often run Windows Server on laptops with both wired and wireless connections. To get Windows Server to correctly identify the domain-connected adapter, I disable the wireless adapter.
Windows Server does allow multiple network adapters to be used. You can aggregate bandwidth using network adapter teaming. You can configure upwardly to 32 network adapters to work together.
How Many Tcp Connections Can A Windows Service Handle Windows Server 2012,
Source: https://www.microsoftpressstore.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2217263
Posted by: pressleyolawkway.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Many Tcp Connections Can A Windows Service Handle Windows Server 2012"
Post a Comment